(Research paper submitted to the International Conference on Big Data, IoT, and Machine Learning)
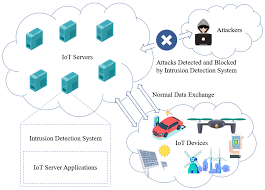
Abstract: As the field of cybersecurity continues to evolve with evercomplex cyber-attacks, older-generation intrusion detection systems have become less and less viable in confronting the challenges posed by these attacks. Thus, the proposed Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
aims to enhance deep-learning models with a feature-wise attention mechanism. This objective expounds on the idea of increasing detection accuracy by allowing models to dynamically shift their focus on the application of the most informative features from the perspective of network
traffic data. We have investigated and implemented three different deep learning architectures: Recurrent Neural networks (RNN)-based attention, Gated Recurrent Units (GRU)-based attention, and Long ShortTerm Memory (LSTM)-based attention, which will capture time dependencies and will emphasize the input dimensions that are important. The XGBoost classifier is also included and serves as the comparison baseline for a machine learning model. Training and evaluation is performed using the SE-CIC-IDS 2018 dataset, which captures a considerable crosssection of real-life attack types. Data preprocessing techniques, including feature selection, normalization, and class balancing, were exhaustively performed to improve data quality and thereby enhance model performance. Results from the experiments showed that the LSTM model with attention had the best result in classification performance, producing fewer false positives than any other architecture. The study considerably contributes to differentiating and discerning NIDS perstormers with thanks to attention mechanism applications.
Posted in Deep Learning, Machine Learning